|
Origin
- Varied opinions are held regarding the exact land of origin
of the castor plant. Some workers view that though castor
is cultivated throughout India, Yet it is indigenous to Africa.
- Castor is native to India by some workers.
- They hold this view mainly on the basis of knowledge of the
medicinal uses of this plant as found in Sanskrit literature.
- Some workers toured to India and found some evidence only
at the foot of Himalayas to show that castor is a native of
India.
- They therefore believes that it may have originated in India
as well as in Africa.
- Hindus have known castor oil from very remote periods.
- This oil has been mentioned in Susruta Ayurveda, one of the
oldest works on Ayurveda.
- It is therefore possible that castor has originated both in
India and Africa.
Scientific Names
Latin :
Ricinus communis
French :
Huile de castor, Ricin de palma
German :
Ricinus semenol
Local Names
|
Language
|
Name
|
| Hindi
|
Erand, Arand |
| Bengali
|
Bherenda |
| Assamese
|
Eri, Era gatch
|
| Nepalese
|
Areta, Alha
|
| Bihari
|
Airar. Anda
|
| Oriya
|
Gab |
| Rajasthani
|
Arend |
| Marathi
|
Erandi |
| Gujarathi
|
Diveligo, Diveli
|
| Malayalam
|
Ayanakku |
| Tamil
|
Amanakku, Kottamuthu
|
| Sanskrit
|
Rakt erand,Vatahari
|
| Telugu
|
Amudam, Amdi.
|
 Top
Top
Distribution
- The world area and production statistics for castor seed
are fluctuating every year.
- The main castor seed producing countries are Brazil,
India and Argentina.
- Other countries growing castor include Indonesia,Indo-China,
Madagascar, Angola and Mozambique.
- During the Second World War the crop was also developed
in Mexico and Japan.
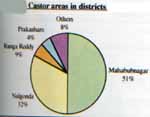
Telangana
- This is by far the most important area now for castor
production in India.
- It is sown in July-August and harvested from January
to March.
- The crop is concentrated mainly in Mahaboobnagar and
Nalgonda districts.
In the Telangana, castor is sown as a pure crop.
Mixtures are rare.
- Here it is mostly raised as a pure crop but mixtures
of castor with Jowar, bajra, groundnut and ragi, are
also to be found.
Bihar
- The production of castor seed in this state is mainly
concentrated on the banks of rivers particularly the Ganges.
- Of the total estimated production, about 40 per cent is contributed
by Bhagalpur district, 14 per cent by Purnea and Monghyr,
30 per cent by the western districts of Suran, Champaran and
Muzaffarpur.
- The balance is drawn from the districts of Darbhanga, Patna
and Gaya.
- In the eastern districts, a pure crop is in vogue more than
mixtures.
- The crop is sown in September-October and harvested in March
- April.
- In the western districts, mixtures are more common and raised
both in the kharif (monsoon) and rabi (winter) seasons.
- In Kharif, castor is mixed with maize, Red gram or cotton
and in rabi with mustard, peas potatoes or chillies.
Gujarat
- Of the total production, nearly 70 per cent comes from
Kathiawar and Gujarat.
- Castor crop is important in Junagadh, Nawanagar, Kutch, Ahmedabad,
Surat, East Khandesh and Kaira.
- In the other areas, castor crop is mostly raised as a pure
crop.
- If sown as mixtures, it is mixed with cotton, jowar, bajra
and sesamum.
- Sowings are done in June-July and harvesting in December to
February.
Tamilnadu
- Salem is an important districts for castor and to a smaller
extent Coimbatore, Tiruchirapally and North Arcot districts
as well.
- About one-third of this is grown as pure, while the rest is
sown as mixture with Sorghum, bajra and groundnut, ragi, etc.,
Castor is also sown along the borders of sugarcane fields
as well as a shade crop for turmeric fields and chillies.
Uttar Pradesh
- Of the total production, 20 per cent is drawn from northern
district of Lakhimpur, 6 per cent from sitapur and Bahraich,
30 per cent from the central districts of Etawah, Kanpur,
Fathepur and allahabad.
- The major portion of the balance is produced in the southern
districts of Jalaun, Banda and Hamirpur.
- About 95 per cent of the crop is raised as Kharif which is
sown in June-July and harvested between February and April.
- As a mixture, it is raised with maize, arhar, jowar, bajra
and cotton.
Mysore
- The crop is mostly concentrated in the Chitradurg, Tumkur,
Mysore and Bangalore districts which, together, cover more
than 80 per cent of the total area under castor in the state.
- The crop is generally sown as a mixture with jowar, ragi,
lablab etc.
- In some parts of Bangalore district, sowing is done in July
and crop harvested from January to March, whereas in Mysore
district sowings commence in April-May and crop is harvested
in October-November.
Other Areas
- The other growing areas including Assam, Bengal, Madhya
Pradesh, Orissa, part of the Punjab.
- In Assam, Castor is mainly raised to feed the Eri silk worm.
 Top
Top
Area and production
 |
- Castor (Ricinus communis) plays an
important role in the country's vegetable oil
economy.
- Today Castor oil finds application in the manufacture
of a wide range of ever expanding industrial products
such as nylon fibres, jet-engine lubricants, hydraulic
fluids and a host of similar others.
|
- Despite phenomenal increase witnessed in the production
and productivity of castor over the last ten years,
there still exist wide regional disparities in the per
hectare yields of castor.
- A multitude of factors such as its cultivation in
submarginal and marginal lands under rainfed conditions
with practically little or no inputs, use of poor quality
seed and inefficient crop management are rersponsible
for such dismal yield.
- The area under castor in Composite A. P. is gradually
declined along with other crops in the last five decades.
- Ruling varieties and hybrids include Aruna, Sowbhagya,
Bhagya, Kranti, GCH-4 and others. No significant change
can be observed in the production of castor over the
last five decades.
World Area, Production and Productivity during
2012
| Country |
Area in Ha. |
Production in Tonnes
|
Productivity (kg/ha)
|
|
World
|
1689335
|
1959637
|
1160
|
|
Angola
|
16000
|
4000
|
250
|
|
Brazil
|
84390
|
25989
|
308
|
|
China
|
190000
|
170000
|
894
|
|
India
|
1120000
|
1630000
|
1455
|
| Indonesia |
6400
|
2500
|
390
|
| Madagascar |
7500
|
2650
|
353
|
|
Mozambique
|
185000
|
62000
|
335
|
Source: Faostat Citation
Area, Production and Yield of Castor in India
(2011-12)
|
State
|
Area in 000' Ha.
|
Production in 000' Tonnes
|
Productivity (Kgs/ha)
|
Composite Andhra Pradesh
|
254 |
52 |
205 |
| Assam |
1.1 |
0.5 |
429 |
| Bihar |
0.1 |
0.1 |
1000 |
| Gujarat |
878 |
1803 |
2054 |
| Harayana |
1.5 |
1.5 |
1000 |
| Jharkhand |
0.1 |
0.1 |
488 |
| Karnataka |
16.0 |
14.0 |
875 |
| Madhya Pradesh |
1.4 |
0.4 |
286 |
| Maharashtra |
8.0 |
3.0 |
375 |
| Orissa |
12.9 |
8.2 |
636 |
| Rajasthan |
291.2 |
410.1 |
1408 |
| Tamilnadu |
6.2 |
1.9 |
310 |
All India
|
585 |
428 |
7.3 |
Source: DACNET
 Top
Top
Uses Of Castor
Castor Oil
- Castor oil is unique in its chemical composition.
- It remains viscous at high temperatures and liquid at low
temperatures.
- It is a non-drying oil. On account of this, it is considered
as one of the best lubricants and is extensively used in the
manufacture of lubricants.
- Before 1914-1918, railways used to buy large quantities of
castor oil for lubrication. Some of the railways had their
own mills.
- During the last two decades, castor oil has been replaced
to a large extent by mineral oil.
- Castor oil is also used in various industries such as textiles,
flour milling, as lubricant.
- Its medicinal use is known since a long time.
- Castor oil is used for lighting purposes in rural areas and
some of the railways use it for lighting the signal and hand
lamps.
- Castor oil and kerosene are mixed in the proportion of 7 :
1.
- It is estimated that about 5,000 tons of castor oil are annually
utilised in the preparation of sulphonated castor oil, known
as Turkey oil which is used in cotton dyeing, printing and
leather industries.
- About 3,000 tons of castor oil are consumed in the manufacture
of soaps.
- Castor oil imparts a certain degree of transparency to soaps.
- Castor oil soaps impart a shining and silky appearance to
jute fabrics.
- Raw castor oil is used for promoting growth of hair.
- Castor oil is used in the manufacture of refined and perfumed
hair oil.
- It is estimated that about 2,000 tons of castor oil are utilised
for this purpose.
- Dehydrated castor oil is the largest new development for conversion
to Sebacic acid, an important ingredient for the synthesis
of Nylon fibre.
- Castor oil or its derivatives are used in the manufacture
of disinfectants such as phenyles.
- About 1,000 tons of castor oil are consumed in this industry.
- The use of castor oil as a purgative is well known.
- About 2,000 tons of oil are consumed for medicinal purposes.
- In rural areas, castor oil obtained by boiling the seed, is
considered better.
In medicinal uses, castor oil has to satisfy the British Pharmacoepia Standard as shown below :
| Specific gravity at 15.5
0 C
|
0.958 to 0.969
|
| Saponification
value
|
177 to 187
|
| Refractive
index at 4000 C
|
1.4695 to 1.4730
|
| Acid value
|
Not more than
4
|
| Iodine value
|
82 to 90
|
- The oil for medicinal purposes is required to remain bright
when cooled to 00C and kept at that temperature for 3 hours.
- Its optical refraction should not be less than three to five.
Castor cake
- There have been no imports of castor cake.
- Before 1914-1918, United Kingdom and some other countries
took some castor cake from India, but in recent years, the
exports to other destinations have been negligible.
- But Ceylon is the only buyer outside India.
- The entire quantity of castor cake available is used as manure
as it contains 4.5 per cent of nitrogen.
- Castor cake is mostly used for sugarcane fields as this cake
is not attacked by white ants.
 Top
Top
|
